Reliable data pipelines are the backbone of modern analytics, machine learning, and reporting systems. When pipelines fail or degrade, downstream decisions and user experiences suffer. This article explores pragmatic operational insights to keep pipelines healthy, scalable, and predictable. The guidance focuses on measurable observability, prevention of cascading failures, and processes that turn incidents into lasting improvements.
Measuring what matters
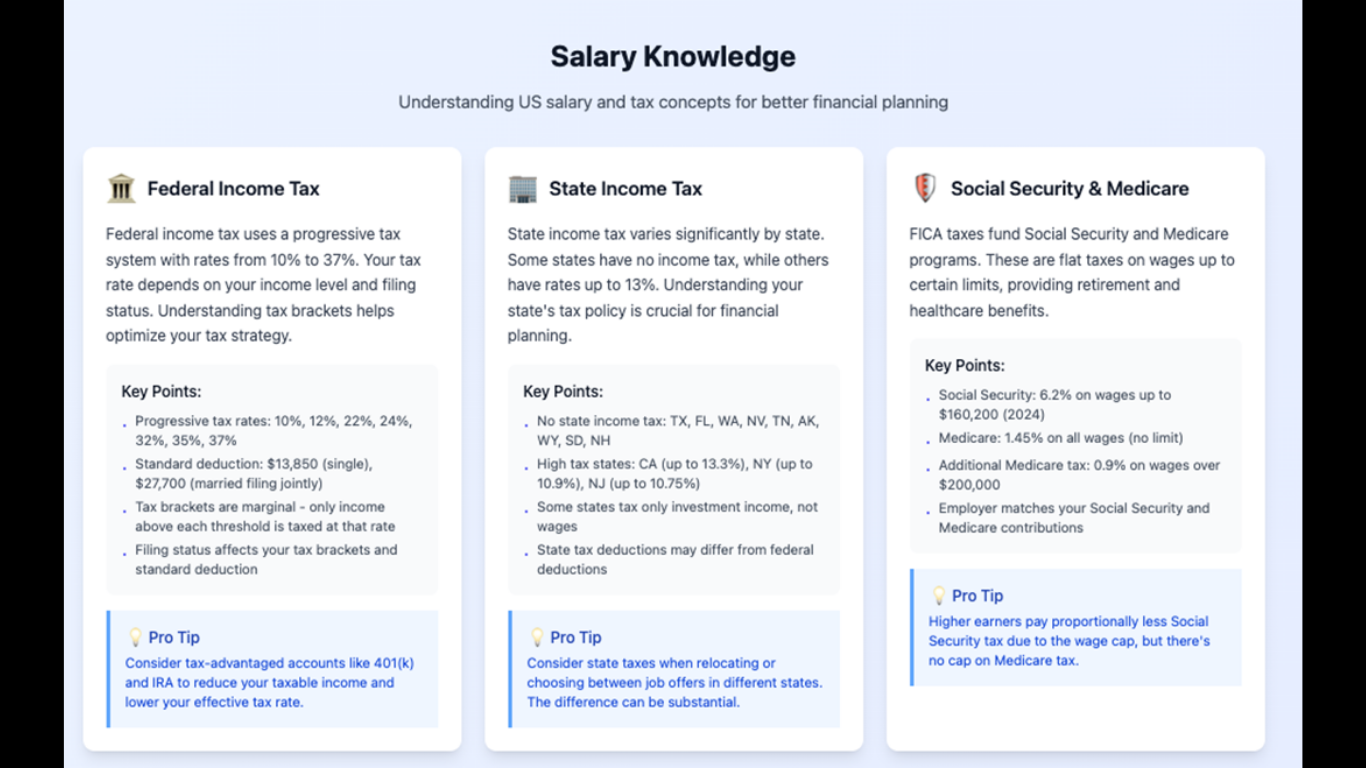
Effective performance management begins with defining the right signals. Throughput, latency, error rates, and data freshness are core metrics, but teams often miss the business-context layer: the impact of delayed or missing records on revenue, compliance, or customer experience. Establish service-level indicators that tie technical metrics to business outcomes, then continuously monitor trends rather than only threshold breaches. Instrumentation should surface signal quality as well as system health, because a pipeline that runs in time but produces corrupt or incomplete outputs is still failing the business.
Instrumentation and tracing
Comprehensive instrumentation lets operators quickly locate the source of a problem. Collect end-to-end traces for typical data flows so you can follow a record from ingestion through transformation to consumption. Capture metadata such as data schema versions, partition keys, offsets, and processing timestamps. Implement observability hooks at connector boundaries and key transformation stages, and aggregate logs, metrics, and traces into a single pane. Many teams augment those streams with real-time data observability dashboards that correlate events and surface anomalies before they escalate. Correlating these signals reduces mean time to detection and mean time to repair.
Resilience patterns for stability
Design pipelines to tolerate transient failures and to recover gracefully. Idempotent processing prevents duplicate side effects when retries are necessary. Backpressure mechanisms throttle upstream sources when downstream systems are overloaded, avoiding queue explosions that lead to catastrophic drops. Partitioning and sharding strategies should balance load while minimizing cross-partition coordination overhead. Implement dead-letter handling to separate problematic records for human review without blocking healthy flows. Additionally, design clear retry policies and exponential backoff to reduce thrash in distributed systems.
Operational playbooks and runbooks
When an incident occurs, having a well-practiced playbook shortens recovery time and reduces cognitive load on responders. Runbooks should describe triage steps, common checkpoints, and safe rollback or mitigation options. Include queries to validate data integrity, commands to inspect connector offsets, and steps to reprocess data when necessary. Practice tabletop exercises and post-incident reviews focusing on what controls failed, what signals were missing, and what safeguards could prevent recurrence. Embed decision trees for escalation so on-call engineers know when to involve storage, network, or consumer teams.
Capacity planning and cost-performance balance
Operational robustness requires planning for peak loads and graceful degradation. Use historical telemetry to model traffic growth and worst-case scenarios, then validate those models through load testing. Balance cost against performance by classifying data flows: critical real-time streams may justify higher-cost low-latency infrastructure, while batch processes can be scheduled on cheaper, elastic resources. Tagging pipeline components with business priority allows orchestration systems to make automated scaling and preemption decisions that align with organizational objectives.
Data quality and validation
Prevention of bad data is as important as catching system faults. Implement schema validation, checksums, and fingerprinting at ingestion to detect drift. Apply lightweight statistical tests to flag anomalies such as sudden spikes in null values or distribution shifts. When transformations occur, assert invariants like monotonic timestamps or domain-specific constraints. Automate alerting for violated assertions and couple alerts with suggested remediation steps. A culture where producers and consumers share responsibility for data quality reduces blame games and accelerates fixes.
Continuous improvement and feedback loops
Operational excellence is iterative. Use incident metrics—time to detect, time to mitigate, recurrence rate—as inputs into prioritization. Automate post-incident analysis by capturing a timeline of relevant telemetry, which makes root-cause analysis faster and more objective. Regularly review alerts to minimize noise and tune thresholds to current baselines. Invest in developer experience for operators: clearer logs, more actionable alerts, and self-service reprocessing tools shorten time from problem discovery to resolution.
Collaboration across teams
Robust pipelines require cross-functional ownership. Architects, platform engineers, data producers, and analysts must agree on contracts, SLAs, and deployment practices. Establish calendar-free zones or change freezes during critical reporting windows, and use feature flags for gradual rollout of changes to pipeline logic. Create a governance forum to standardize observability practices, schema evolution policies, and incident response protocols so that improvements scale across projects rather than remaining tribal knowledge.
Final considerations for operational maturity
Achieving sustained pipeline performance is a balance of technology, process, and culture. Prioritize visibility, resilience, and repeatable operations. Embed instrumentation early, practice response plans regularly, and align metrics to business outcomes. Over time, these investments pay dividends through reduced downtime, faster recovery, and more trust in data products. Robust pipelines free teams to focus on innovation rather than firefighting, and they transform data from a liability into a dependable asset.
Article received on email